Introduction
Welcome to our comprehensive guide on managing and treating type 2 diabetes. Type 2 diabetes is a chronic condition that affects millions of people worldwide, and can lead to serious complications if not properly managed. Our team of experts has compiled the most up-to-date and evidence-based information to help you understand the causes, symptoms, and stem cell treatment options for type 2 diabetes.
Understanding Type 2 Diabetes
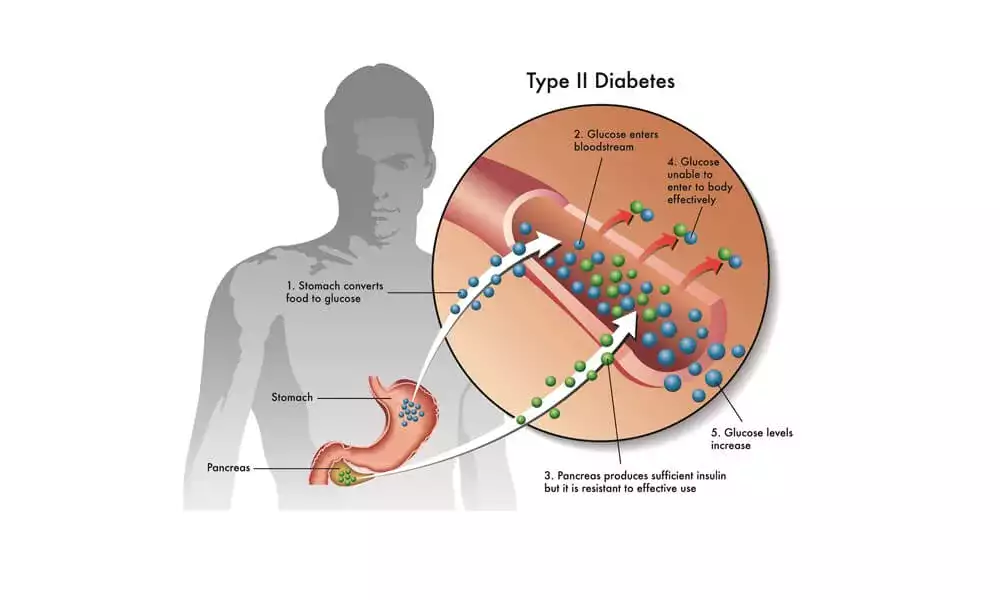
Type 2 diabetes is a metabolic disorder characterized by high blood sugar levels resulting from insulin resistance or insufficient insulin production. Insulin is a hormone that regulates blood sugar levels, and when the body becomes resistant to insulin, it cannot effectively control blood sugar levels. Over time, high blood sugar levels can lead to severe complications, such as cardiovascular disease, kidney disease, nerve damage, and blindness.
Symptoms of Type 2 Diabetes
The symptoms of type 2 diabetes can vary from person to person, but some of the most common symptoms include:
- Frequent urination
- Increased thirst
- Unexplained weight loss
- Fatigue
- Blurred vision
- Slow healing of cuts and bruises
If you are experiencing any of these symptoms, it is essential to seek medical advice and get tested for diabetes.
Diagnosis of Type 2 Diabetes
To diagnose type 2 diabetes, your healthcare provider will perform a blood test to measure your blood sugar levels. If your blood sugar levels are higher than normal, your provider may perform additional tests to confirm the diagnosis.
Managing Type 2 Diabetes
Managing type 2 diabetes requires a comprehensive approach that includes lifestyle modifications, medication, and regular monitoring. The following strategies can help you manage your type 2 diabetes:
- Eating a healthy, balanced diet that includes plenty of vegetables, fruits, and whole grains
- Regular exercise, such as brisk walking or swimming
- Taking medications as prescribed by your healthcare provider
- Monitoring your blood sugar levels regularly and keeping track of your results
- Quitting smoking and avoiding excessive alcohol consumption
- Regular visits with your healthcare provider to monitor your condition and adjust your treatment plan as necessary
Treatment Options for Type 2 Diabetes
There are several treatment options for type 2 diabetes, including:
Oral medications: These medications help lower blood sugar levels and improve insulin sensitivity.
Insulin therapy: Some people with type 2 diabetes may require insulin therapy to control their blood sugar levels.
Lifestyle modifications: Eating a healthy diet, exercising regularly, and losing weight can help improve blood sugar control.
Bariatric surgery: For people with obesity and type 2 diabetes, bariatric surgery may be an effective treatment option.
Stem Cell Treatment: Stem cells are unique cells that have the ability to develop into different types of cells in the body. In the context of diabetes treatment, stem cells can be used to generate new insulin-producing cells or to help repair damaged cells in the pancreas.
Conclusion
Type 2 diabetes is a chronic condition that requires ongoing management to prevent complications. By making healthy lifestyle choices, taking medications as prescribed, and working closely with your healthcare provider, you can effectively manage your type 2 diabetes and improve your overall health and well-being. If you have any concerns or questions about managing your diabetes, please consult with your healthcare provider for personalized advice and guidance.
Read More: Stem Cell Therapy: What You Need to Know